Welcome to our Blog about Hepatitis C of in short “Hep C” which is a complicated but at the same time interesting disease for doctors and reasearch fellows at leading universities worldwide all with the focus to find the better and best treatment.
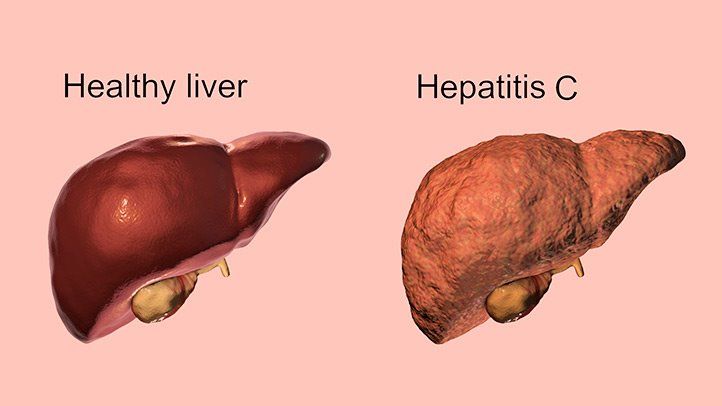
What exactly is Hep C?
Firstly as there is Hep C, there probably also should be hepatitis A and B and you are absolutely right these diseases also there, but not the focus of our blog. However we will also discuss them lateron we want to give you the full picture. Generally speaking, Hepatitis C is a viral liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus that causes liver swelling, called inflammation. It can lead to chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and in severe cases, liver failure or liver cancer. Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, long-term illness. Hepatitis C is often described as “acute,” meaning a new infection, or “chronic,” meaning long-term infection. Most people suffer from chronic Hep C.
How do you get Hepatitis C?
As the hepatitis C virus is a bloodborne virus, which means it is transferred by blood. Most Hep C infections occur through exposure to blood from unsafe injection practices, unsafe health care, unscreened blood transfusions, injection drug use and sexual practices that lead to exposure to blood to the virus. So if you have sex with someone who has the hep C virus, there is a big chance you will also get it. While there is a vaccine for hepatitis B, unfortunately there is no vaccine for hepatitis C. On the other hand there are medications available which is a big plus!
Hepatitis C treatment
For treatment of Hep C as mentioned there is no vaccine available for prevention, but there are antiviral medications available. Historically, treatment options for hepatitis c were limited and often had significant side effects, however thanks to research and hard work currently top medicine are available for effective treatment including sofosbuvir ( which are sold under the brand names: Harvoni and Sovaldi), ribavirin ( which is sold under the names: Rebetol and Copegus), and daclatasvir (market under the brand: Daklinza), are used to treat hepatitis C. Some people’s immune system can fight the infection on their own and new infections do not always need treatment. It is important to regularly test your blood to see if you have disseaes in general, but especially for hepatitis A, B and C, because the earlier you start treatment the better.
Past Treatments:
Earlier treatments relied on interferon-based regimens, which were associated with challenging side effects and limited efficacy, often requiring lengthy durations of therapy. The introduction of Direct Acting Anti-virals ( also called DAAs ) revolutionized hepatitis C treatment. These medications directly target the virus, disrupting its replication process, and have shown exceptional efficacy, with high cure rates and fewer side effects compared to previous therapies.
Current Treatments:
DAAs have demonstrated cure rates exceeding 95% in most cases, marking a significant improvement over previous treatments. Achieving sustained virologic response (SVR), where the virus remains undetectable in the blood for a certain period post-treatment, indicates a successful cure.
Acute Hepatitis C
Acute hepatitis C is a viral infection caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver. Acute hepatitis C often presents as a mild or asymptomatic illness, making it challenging to detect without specific testing.
Acute Hep C Symptoms:
However, some individuals may experience the following symptoms:
- Flu-like symptoms such as fatigue, fever, and muscle aches
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
It’s important to note that symptoms might not appear immediately after infection and can take several weeks to months to manifest.
Chronis Hepatitis C
Chronic hepatitis C is a persistent infection caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that affects the liver, potentially leading to long-term liver damage, cirrhosis, and an increased risk of liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis C develops when the HCV infection persists for six months or longer.
Chronic Hep C Symptoms:
Chronic hepatitis C often progresses slowly and may remain asymptomatic for years. When symptoms do occur, these might include the following:
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dark urine
- Easy bruising or bleeding
Conclusion
We discussed what is hepatitis C, How you get it, what are the treatments, the difference between acute and chronic hep C and the symptoms. While hepatitis C was and remains a serious and dangerous disease, fortunately both for acute and chronic Hep C there are various medications available, thanks to advancements in treatments such as direct-acting antivirals (DDAs). Early diagnosis, timely intervention, and access to effective treatments play pivotal roles in preventing complications, preserving liver health, and improving the overall quality of life for individuals affected by chronic hepatitis C. For those who want to dive deeper into the subject of Hepatitis C, we have a Blog page with articles and various links to treatments and medications for you to read more and we strongly encourage you to do so, as we say in the field of medicines it is always better to know more and dive deeper.